Introduction to SDDC is an article that explains the core fundamentals of SDDC. SDDC is an acronym for Software-Defined Data Center and it’s very common in the documentation about Data Centers based on Software-Defined.
What is SDDC?
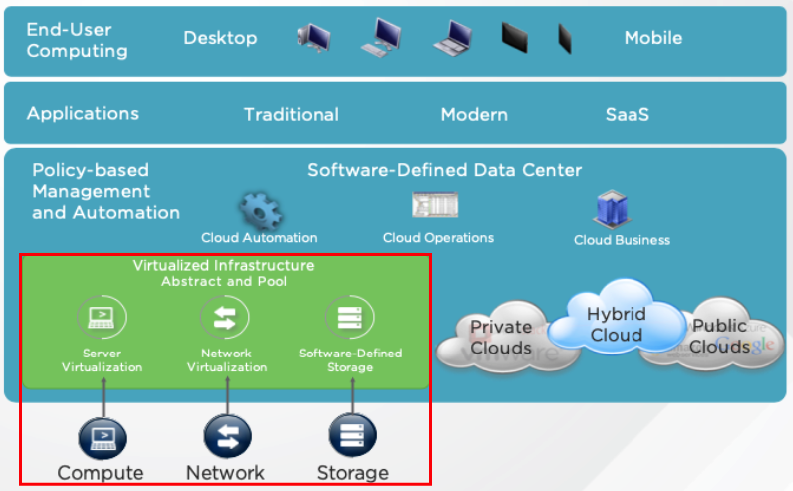
SDDC is a concept used in IT to refer to data center infrastructures based on virtualization, such as Computing, Storage, and Networking.
With virtualization, it’s possible to abstract the hardware layer and create a Pool of Resources. In this way, resource utilization is improved and we have more scalability.
The term SDDC is more used in “Clouds“.
A “Private Cloud”, for instance, can be considered one private SDDC infrastructure, owned by a company (on-premise).
A “Public Cloud”, can be an SDDC infrastructure based on a public Cloud such as Azure, AWS, or something like that (off-premise).
Additionally, In an SDDC infrastructure, we have some software layers:
- Computing: Responsible for executing the customer’s workloads (VM Virtualization, Containers, etc)
- Storage: Responsible to store the data (SDS = Software-Defined Storage)
- Networking: Responsible to provide the network connectivity (SDN = Software-Defined Network)
Below it’s possible to see an SDDC Architecture. The base of the SDDC Architecture is Software-Defined and all other layers used this base architecture, independent of the hardware layer:
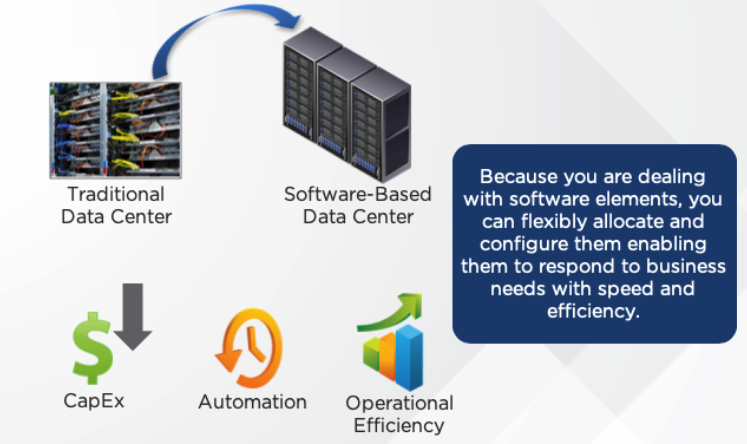
Because you are dealing with software elements, you can flexibly allocate and configure the resources to respond to business needs with speed and efficiency:
Compute Virtualization
Compute virtualization, also called server virtualization, is the first step toward SDDC:
- Compute virtualization offers greater efficiency
- The CPU and memory are decoupled from physical hardware, creating pools of resources for use, wherever needed
- Each virtualized application and its operating system are encapsulated in a separate, isolated software container called VM (Virtual Machine)
Network Virtualization
Network Virtualization, also known as SDN (Software-Defined Network), decouples network resources from the underlying hardware. Here, we have the same physical network devices, but in a virtualized way:
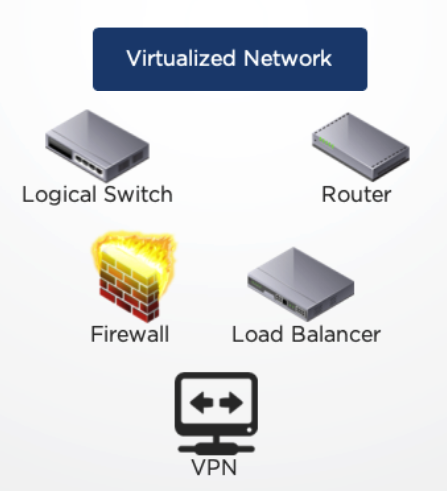
- A virtualized network is a software container that presents logical network components to connected workloads
- Virtualized networks are programmatically created, provisioned, and managed, with the underlying physical network serving as a simple packet-forwarding backplane
- Network and security services are allocated to each virtual machine according to its needs and stay attached to it
Storage Virtualization
Storage virtualization or SDS (Software-Defined Storage) transforms storage in virtualized environments by aligning it with application demands:
- This transformation’s possible through the hypervisor kernel (in the hypervisor kernel there are necessary modules to implement the Software-Defined Storage):
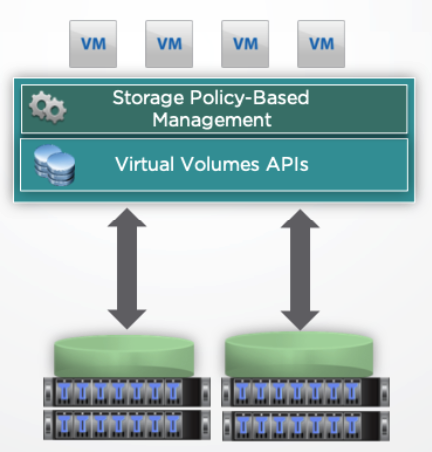
SDDC Features
The SDDC infrastructure can be there a lot of features. But, at least, we can describe four important features of SDDC:
- Efficiency
- Control
- Agility
- Choice
Efficiency:
SDDC delivers efficiency, by bringing together virtualized computing, network, and storage with analytics-based operations management and automated operations. This facilitates huge CapEx and OpEx savings, resulting in data centers with costs similar to public cloud providers.
Control:
SDDC delivers control by providing the right availability and security for every app or service with policy-based governance. It also enables the highest levels of application uptime, through automated business continuity. Together with virtualization-aware security and compliance, this helps reduce application downtimes, allowing a private cloud infrastructure to run as per an organization’s specification, where IT administrators define the availability of, and security for each application.
Agility:
SDDC delivers agility, by enabling on-demand, policy-driven deployment of IT services at the speed of business, in turn leading to increased customer satisfaction. It also offers automation of application provisioning and enables self-service on heterogeneous platforms.
Choice:
SDDC provides choices to IT by offering capabilities to run new and existing apps across multiple platforms and clouds. It can be implemented as a private, hybrid, or public cloud and allows freedom to leverage multiple hardware or software stacks, which leads to the choice of having any app, on any platform, or cloud.
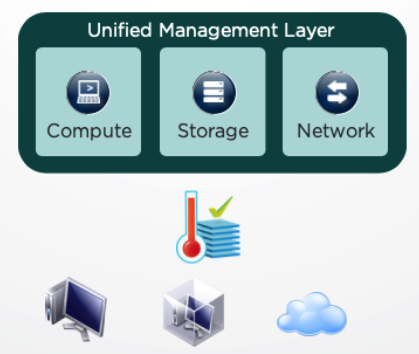
Unified Data Center Management
The final facet of SDDC is wrapping the virtualized infrastructure in a unified management layer:
- The management layer vastly simplifies governance and operations
- A single, unified management platform lets you centrally monitor and administer all applications across physical geographies, heterogeneous infrastructure, and hybrid clouds
- You can deploy and manage workloads in physical, virtual, and cloud environments
So, to get more detail about SDCC, I recommend the short course “Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) Overview”: