A little Introduction about VxRail is an article that details the hyper-convergence solution called VxRail.
Firstly, when discussing hyper-convergence infrastructure, we discuss a converged architecture defined as software. We have some layers in this architecture, and each layer is managed by software.
About the layers, they are:
- Computing: Responsible for executing the customer’s workloads (VM Virtualization, Containers, etc)
- Storage: Responsible to store the data (SDS = Software-Defined Storage)
- Networking: Responsible to provide the network connectivity (SDN = Software-Defined Network)
We have an article that introduces the SDDC concept (Software-Defined Data Center). I believe that this article is a good point to understand a bit more about SDDC, and of course, about hyper-convergence architecture. Click here to read this article.
Additionally, the video below introduces what is HCI:
Basically, What is VxRail?
VxRail is a hyper-converged solution owned by Dell Technologies and is the only jointly engineered hyper-converged infrastructure system with VMware.
Powered by VMware vSAN and managed through the VMware vCenter interface, VxRail provides
existing VMware customers with a consistent operating experience. As the foundation for Dell
Technologies Cloud, VxRail is the first hyper-converged system fully integrated with VMware Cloud Foundation SDDC Manager to deliver one, complete, automated platform.
As we said, the VMware vSAN is responsible to create the storage repository for all VMs and other objects.
In a VxRail Cluster, all nodes have a Dell Hardware Platform (like a PowerEdge Server), the Operating System is the ESXi (managed by the vCenter Server), and all Management is centralized into the VxRail Manager VM. The VxRail Manager VM is fully integrated with vCenter Server when it is possible to manage the cluster with a single panel (vCenter Interface).
Generally, each node (each Hardware Server) is connected to a least one TOR Ethernet Switch. For redundancy purposes, two TOR switches are recommended.
I highly recommend that you read the VxRail Spec Sheet:
https://www.delltechnologies.com/asset/en-us/products/converged-infrastructure/technical-support/h16763-vxrail-spec-sheet.pdf
And of course, the VxRail Data Sheet to get more detail:
https://www.delltechnologies.com/asset/en-us/products/converged-infrastructure/technical-support/vxrail-datasheet.pdf
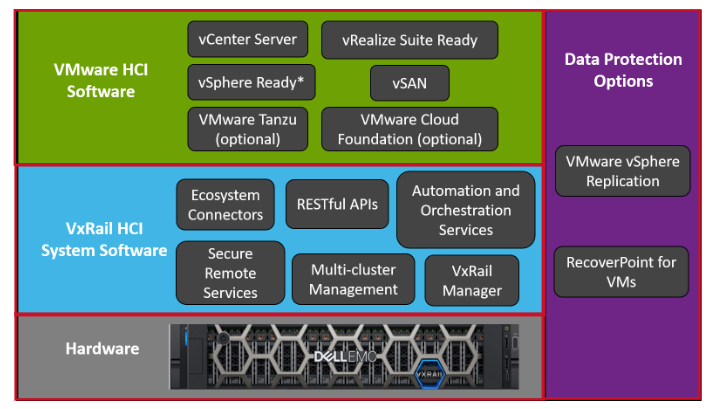
So, I would like to share a picture that provides details about the entire VxRail Architecture.
As we can see in the below picture, the VxRail Architecture is composed of a lot of Software:
VxRail Models
VxRail is offered in multiple models with configuration options including the choice of Intel Xeon Scalable processors, AMD EPYC processors, NVMe drivers, NVIDIA graphics cards, and more.
Below, we have a little more detail about each Model of the VxRail and a brief description of that:


About VxRail Clusters
A VxRail cluster can have from 2 to 64 nodes in the same cluster.
We have the following types of Cluster:
- VxRail vSAN Clusters: vSphere Clusters that use vSAN as the Primary Storage.
- VxRail Dynamic Node Clusters: vSphere Clusters that use external storage as the Primary Storage (this is a Compute-Only vSphere Cluster).
- VxRail Satellite Nodes: Enable customers to implement a low-cost single-node option and benefit from the same VxRail automation, testing and optimization, unique lifecycle management, and deep VMware integration increasing operational efficiencies and standardization across edge locations, without the use of vSAN.
VxRail vSAN Clusters
Here, we have some deployment choices:
vSAN Standard Cluster:
— Can have from 3 to 64 nodes in the same cluster;
— The first three nodes must have identical configurations.
vSAN Stretched Cluster:
— This is a deployment model in which two or more virtualization host servers are part of the same cluster. However, they are in different geographical locations;
— A Witness Host/Appliance is required (placed in a third fault domain or third geographical site);
— Stretched Cluster delivers continuous availability across a campus or metro-base area.
vSAN 2-Node Cluster:
— We have 2 nodes in this type of cluster;
— This deployment type is a special Stretched Cluster configuration. If there is a failure, the Witness Host/Appliance is the component that provides a quorum for the two data nodes.
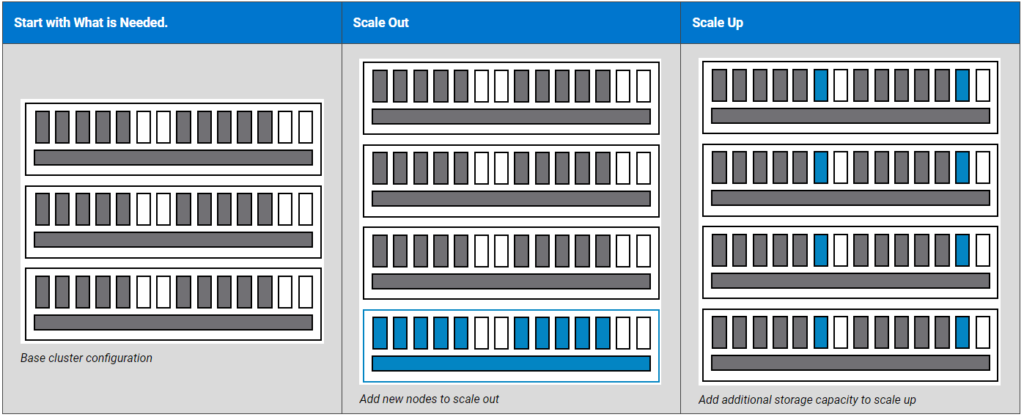
Scaling a VxRail Cluster
One of the many benefits of a VxRail is the ability to start with a small cluster and easily expand it by SCALE-OUT and/or SCALE-UP. Below, we will talk in more detail about each type of scaling:
SCALE-OUT:
— Is the act of adding nodes to the existing cluster;
— VxRail Clusters can start with a few nodes and can be scaled out to 64 nodes;
— Scaling out adds additional Computer/Memory/Storage capacity to the cluster.
SCALE-UP:
— Is the act of adding storage capacity (disks) to the existing nodes;
— In this case, we only increase the Storage capacity.
Maintain Up to Date
So, the VxRail solution is up to date very fast. So, to explore more detail about VxRail and maintain up to date, I recommend the below link:
https://www.dell.com/en-us/dt/converged-infrastructure/vxrail/index.htm?hve=explore#tab0=0&tab1=0