How to enable the vSphere DRS feature is an article to explain how to enable and configure the DRS vSphere on the vSphere Cluster. The DRS is an acronym for Distributed Resource Scheduler and helps to maintain the cluster as balanced as possible related to the CPU, Memory, and network usage.
DRS Introduction
VMware vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) is the resource scheduling and load balancing solution for vSphere. DRS works on a cluster of ESXi hosts and provides resource management capabilities like load balancing and virtual machine placement.
DRS also enforces user-defined resource allocation policies at the cluster level while working with system-level constraints.
The main goal of the DRS is to ensure that VMs and their applications are always getting the computing resources that they need to run efficiently. It does this by ensuring that newly powered-on VMs get all the required resources soon after they are powered on, and the resource utilization is always balanced across the cluster
From time to time, VMs’ workloads may change, and the cluster can be imbalanced. So, in this situation, application performance can be degraded. DRS solves these problems by regularly monitoring the cluster balance state and then taking the necessary actions to fix any imbalance.
DRS on vSphere 7
The new DRS logic in vSphere 7 takes a very different approach. It computes a VM DRS score on each host and moves the VM to the host that provides the highest VM DRS score.
The biggest change from the old DRS version (before vSphere 7) is that it no longer balances the host load directly. Instead, it improves the balancing by focusing on the metric that you care most about: virtual machine happiness.
Important to note that the improved DRS now runs every minute. Before, the DRS runs every five minutes. It is providing a more granular way to calculate workload placement and balancing. This results in overall better performance of the workloads.
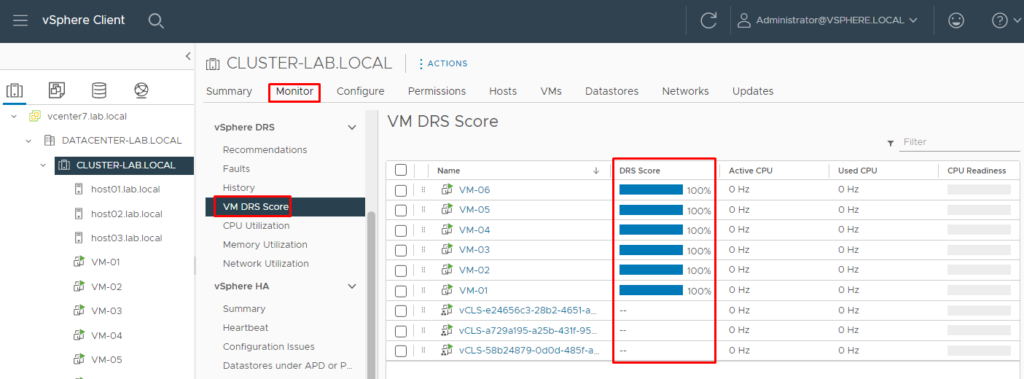
The score values range from 0 to 100% and are divided into buckets; 0-20%, 20-40%, and so on.
Obtaining a VM DRS score of 80-100% indicates that there is mild to no resource contention.
To get more details about the DRS, you can access the link below:
https://core.vmware.com/resource/drs-improvements-vsphere-7#section1
Enabling DRS on the vSphere Cluster
Open the vSphere Client interface, and select the cluster. On the Configure tab go to Services –> vSphere DRS –> Edit.
In our lab, for instance, the cluster name is “CLUSTER-LAB.LOCAL”:
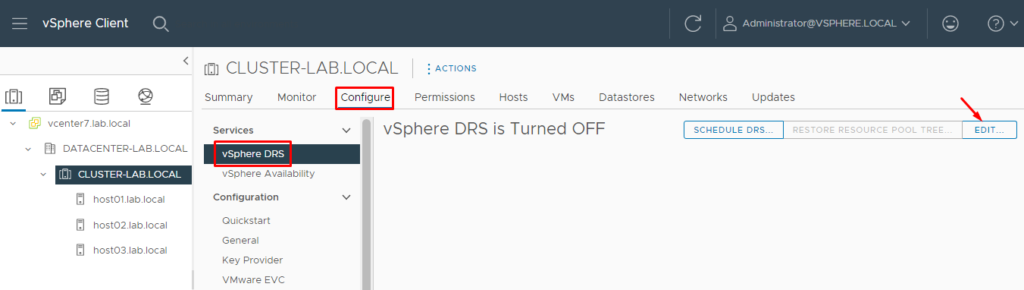
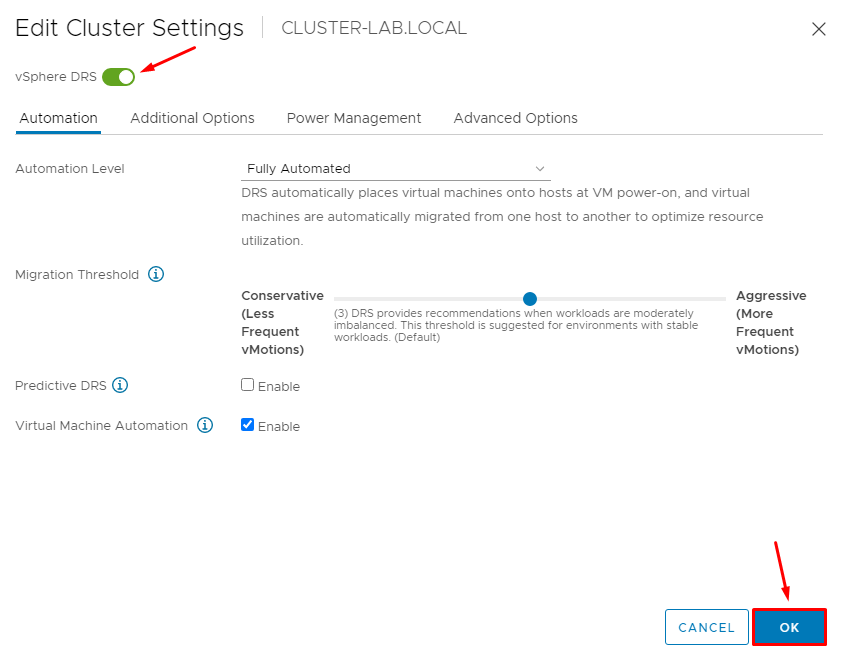
After enabling the DRS service, we can see “vSphere DRS is Turned ON”, demonstrated in the picture below:
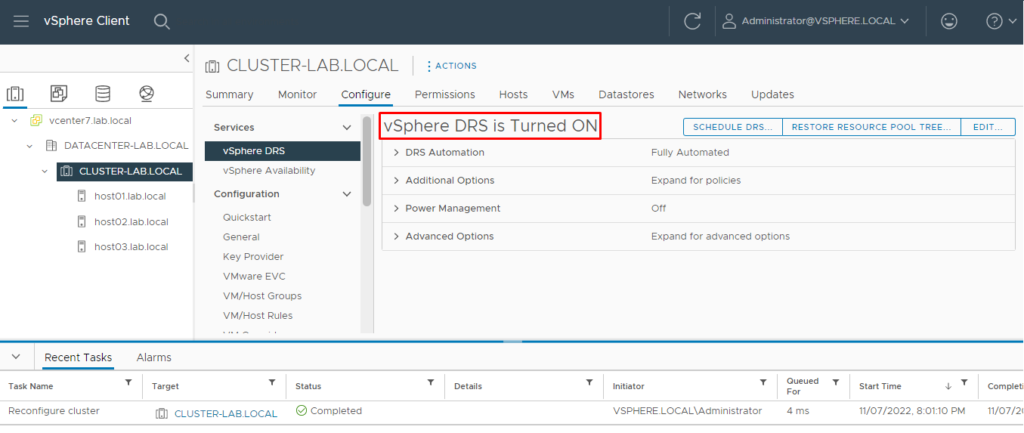
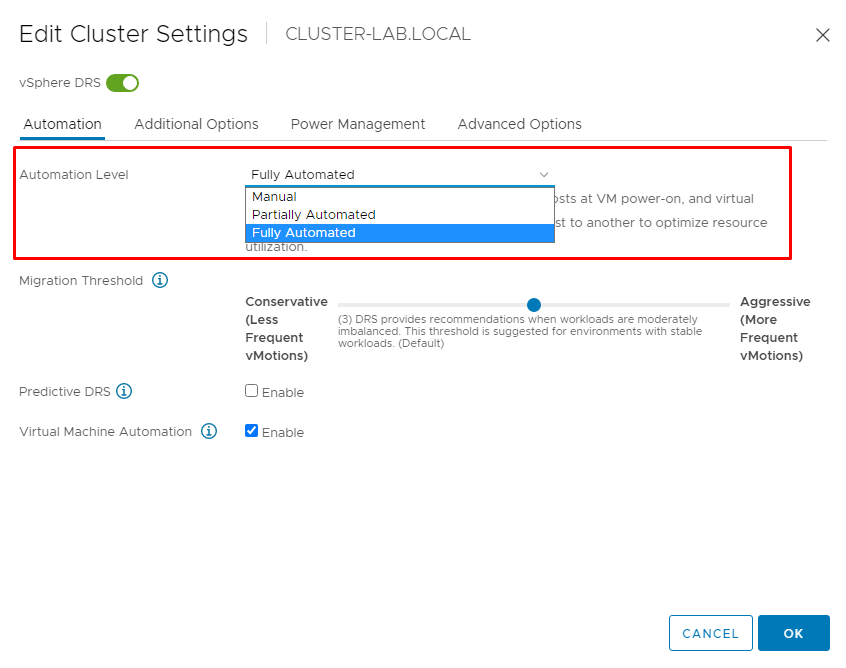
By default, the DRS Automated mode is “Fully Automated”. At this Automation Level, DRS automatically places virtual machines onto hosts at VM power-on, and virtual machines are automatically migrated from one host to another to optimize resource utilization. The other methods of the Automation Level available are:
Partially Automated: DRS automatically places virtual machines onto hosts at VM power-on. Migration recommendations need to be manually applied or ignored.
Manual: DRS generates both power-on placement recommendations, and migration recommendations for virtual machines. Recommendations need to be manually applied or ignored.
To change it, edit the DRS services and choose the best option on Automation Level:
Checking DRS Score
To check the DRS Score for all VMs running in the cluster, select the Cluster –> Monitor –> vSphere DRS –> VM DRS Score:
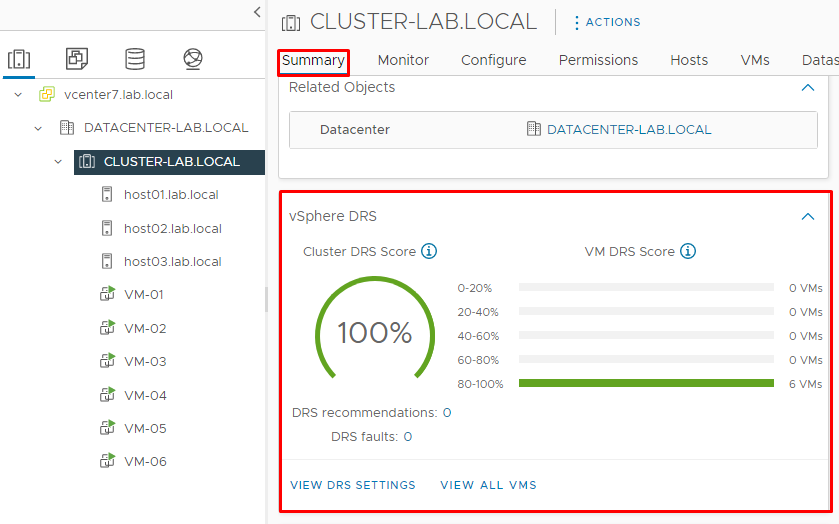
On the Summary tab, it is possible to see the Cluster DRS Score and VM DRS Score, according to the picture below:
Putting the ESXi host in Maintenance Mode
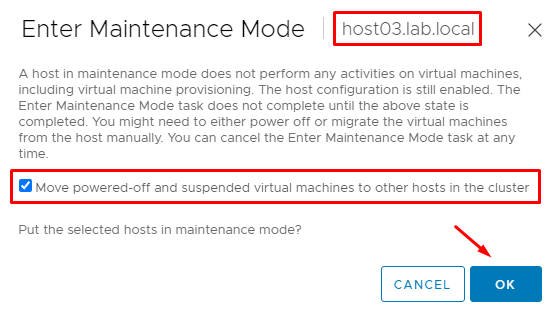
When the DRS is enabled and the Automation Level is Fully Automated, Virtual Machines are migrated automatically when the ESXi host is put in Maintenance Mode (MM).
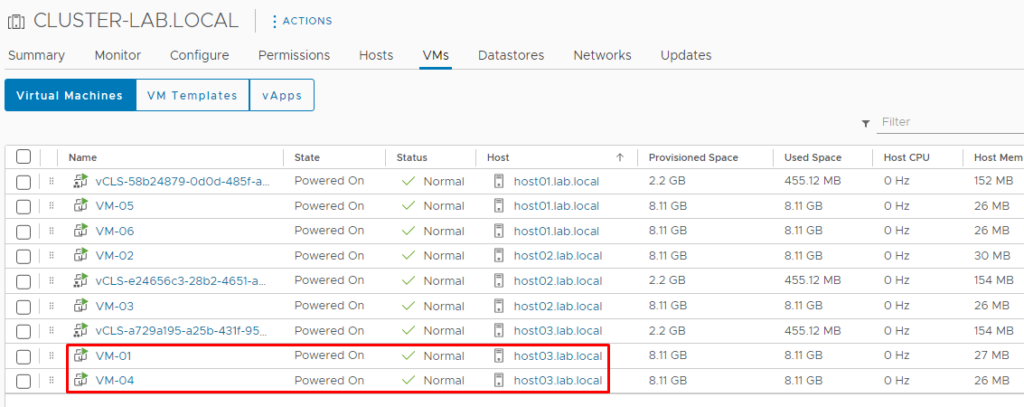
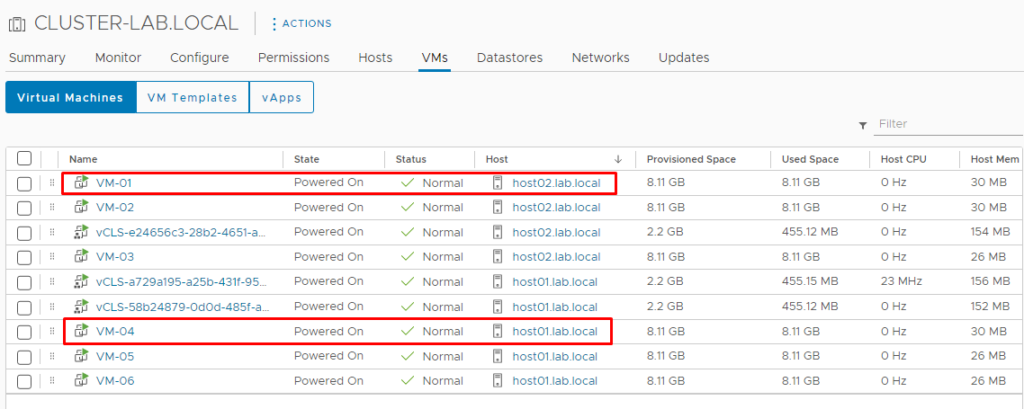
In our lab, for instance, we will put the ESXi host03 in maintenance mode. Observe these VMs “VM-01” and “VM-04”. Both are executing into host03:
Putting the host03 in maintenance mode:
On the “Recent Tasks” on the vSphere Client Interface, we can see both tasks related to the Virtual Machines migration and the task related to the maintenance mode. All tasks have been executed with success by the vCenter Server:
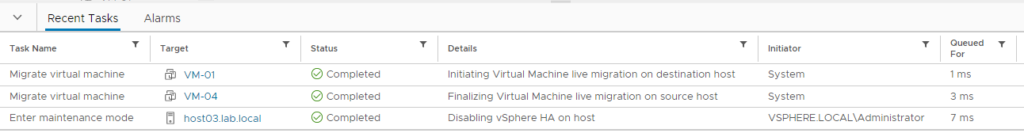
After it, both Virtual Machines in this example (VM-01 and VM-04) are executing in different ESXi hosts:
And the host03 is in maintenance mode:
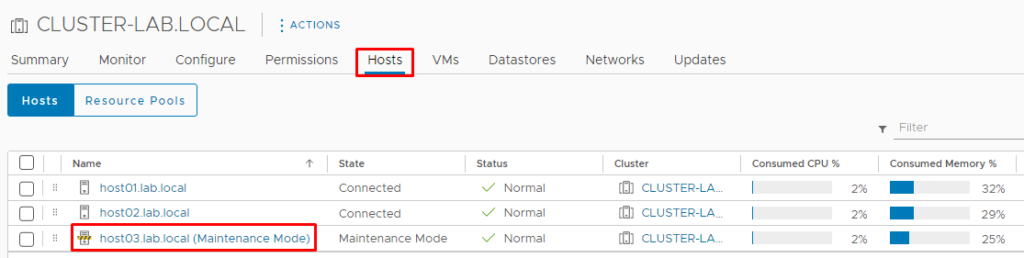
To remove this ESXi host from maintenance mode, Select it and double-click –> Maintenance Mode –> Exit Maintenance Mode.
Note: If DRS Service is enabled but the Automation Level is Partially Automated or Manual, will be necessary to migrate or power off all Virtual Machines for the host to enter Maintenance Mode!