Routing Down on Tier-0 Service Router is an article that explains what happens if a Tier-0 Service Router (SR) loses its routing adjacencies.
As we know, in the NSX world we have two gateway types:
- T0 or Tier-0
- T1 or Tier-1
Both gateways are hosted in the Edge Transport Node device!
Each one is responsible for some activities in the NSX topology and has different characteristics.
We wrote an article that shows some examples of NSX topologies and the meaning of each gateway type and its interfaces. You can access this article by clicking on the following link:
Some Examples of NSX Topologies – DPC Virtual Tips
T0 Service Router (SR)
The Tier-0 Service Router (SR) is responsible for handling the north-south traffic. To do that, uplink interfaces are created and configured in this service router. Commonly, we use dynamic routing protocols to establish adjacencies within the physical routers to provide north-south communication.
In the following picture, we have a lab topology just to explain the concept to you:
- We have both physical routers (router01 and router02). Both are placed outside the NSX environment (outside the virtual “world”);
- We have an edge cluster with four (4) edge transport nodes (edge01, edge02, edge03, and edge04);
- We have a vSAN cluster with three (3) ESXi hosts, already prepared to work as a host transport node.
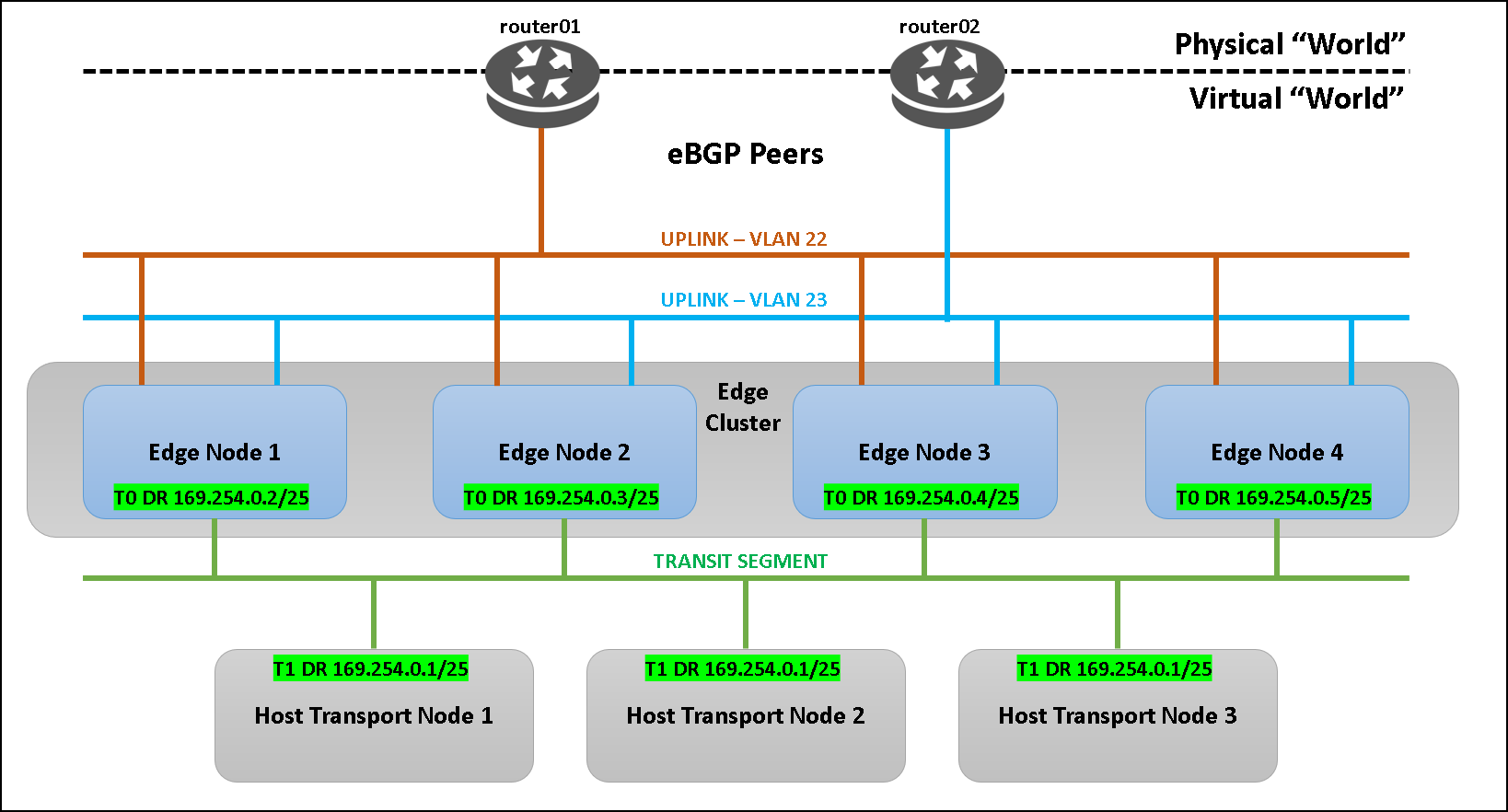
As we can see in the above picture, the “transit segment” is used by the transport node devices (for their internal communication) and an address in the network range 169.254.X.X is assigned for each one. All host transport nodes shared the same address (169.254.0.1), as we can see in the following output. This interface is the LIF (Logical Interface):
HOST-01:
vhost-comp-01.lab.local# nsxcli
vhost-comp-01.lab.local> get gateways
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:42:21.023
Gateways Summary
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VDR UUID LIF num IPv4 Route num IPv6 Route num Max Neighbors Current Neighbors
c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 4 7 5 50000 16
vhost-comp-01.lab.local> get gateway c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 interface
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:42:23.007
Gateway Interfaces
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv6 DAD Status Legend: [A: DAD_Sucess], [F: DAD_Duplicate], [T: DAD_Tentative], [U: DAD_Unavailable]
LIF UUID : ba201756-d373-469c-a309-ee313a4eb9bc
Mode : [b'Routing-Backplane']
Overlay VNI : 73728
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.1/28; fe80::50:56ff:fe56:4452/128(U)
Mac : 02:50:56:56:44:52
Connected DVS : VDS-Computing
Control plane enable : True
Replication Mode : 0.0.0.1
Multicast Routing : [b'Enabled', b'Oper Down']
State : [b'Enabled']
Flags : 0x90308
DHCP relay : Not enable
DAD-mode : ['LOOSE']
RA-mode : ['SLAAC_DNS_THROUGH_RA(M=0, O=0)']
...
...HOST-02:
vhost-comp-02.lab.local# nsxcli
vhost-comp-02.lab.local> get gateways
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:44:56.056
Gateways Summary
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VDR UUID LIF num IPv4 Route num IPv6 Route num Max Neighbors Current Neighbors
c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 4 7 5 50000 11
vhost-comp-02.lab.local> get gateway c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 interface
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:44:58.424
Gateway Interfaces
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv6 DAD Status Legend: [A: DAD_Sucess], [F: DAD_Duplicate], [T: DAD_Tentative], [U: DAD_Unavailable]
LIF UUID : ba201756-d373-469c-a309-ee313a4eb9bc
Mode : [b'Routing-Backplane']
Overlay VNI : 73728
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.1/28; fe80::50:56ff:fe56:4452/128(U)
Mac : 02:50:56:56:44:52
Connected DVS : VDS-Computing
Control plane enable : True
Replication Mode : 0.0.0.1
Multicast Routing : [b'Enabled', b'Oper Down']
State : [b'Enabled']
Flags : 0x90308
DHCP relay : Not enable
DAD-mode : ['LOOSE']
RA-mode : ['SLAAC_DNS_THROUGH_RA(M=0, O=0)']
...
...HOST-03:
vhost-comp-03.lab.local# nsxcli
vhost-comp-03.lab.local> get gateways
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:46:14.946
Gateways Summary
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VDR UUID LIF num IPv4 Route num IPv6 Route num Max Neighbors Current Neighbors
c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 4 7 5 50000 11
vhost-comp-03.lab.local> get gateway c08ecb08-e21e-4d4b-9163-f66d2553bec7 interface
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 13:46:20.098
Gateway Interfaces
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
IPv6 DAD Status Legend: [A: DAD_Sucess], [F: DAD_Duplicate], [T: DAD_Tentative], [U: DAD_Unavailable]
LIF UUID : ba201756-d373-469c-a309-ee313a4eb9bc
Mode : [b'Routing-Backplane']
Overlay VNI : 73728
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.1/28; fe80::50:56ff:fe56:4452/128(U)
Mac : 02:50:56:56:44:52
Connected DVS : VDS-Computing
Control plane enable : True
Replication Mode : 0.0.0.1
Multicast Routing : [b'Enabled', b'Oper Down']
State : [b'Enabled']
Flags : 0x90308
DHCP relay : Not enable
DAD-mode : ['LOOSE']
RA-mode : ['SLAAC_DNS_THROUGH_RA(M=0, O=0)']
...
...Each edge node has an interface using the address on this network (backplane port), as we can see in the following outputs:
EDGE-01:
Interface : 6289a5dc-65c2-40a2-b6bc-53f3bd7b4770
Ifuid : 275
Name : bp-sr0-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-275
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.2/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5300/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:00
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : 1fb264c0-ecd6-4dcc-9856-0f759ec65e62
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :EDGE-02:
Interface : 1207a97d-691a-4db7-b1e0-c9097efb30c8
Ifuid : 275
Name : bp-sr1-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-275
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.3/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5301/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:01
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : df2e0cc7-606c-4100-91e3-ed32ba081d78
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :
EDGE-03:
Interface : 3aad399a-bb37-4d82-81d5-6111b4802863
Ifuid : 285
Name : bp-sr2-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-285
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.4/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5302/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:02
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : 61a1d1b8-3d43-4e01-80e2-1918213b055f
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :
EDGE-04:
Interface : 08b7faef-3aab-421d-9018-a011c7ed1bad
Ifuid : 299
Name : bp-sr3-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-299
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.5/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5303/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:03
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : fda7ed2e-dcd1-4e04-8950-dfab9b7f3500
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :
Additionally, we can access the service router and confirm its BGP neighbors.
For edge-01, for instance, we have both physical routers as neighbors (IPs 10.0.22.1 and 10.0.23.1):
edge-01> get logical-routers
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 14:03:32.358
Logical Router
UUID VRF LR-ID Name Type Ports Neighbors
736a80e3-23f6-5a2d-81d6-bbefb2786666 0 0 TUNNEL 3 3/5000
20169f10-8099-4d27-8915-8e1e0d47e68e 1 2050 DR-T0-GW DISTRIBUTED_ROUTER_TIER0 5 1/50000
c9e7c979-0d69-4aab-bd6c-9ee863c96070 2 3074 SR-T0-GW SERVICE_ROUTER_TIER0 7 5/50000
edge-01> vrf 2
edge-01(tier0_sr[2])> get bgp neighbor summary
BFD States: NC - Not configured, DC - Disconnected
AD - Admin down, DW - Down, IN - Init, UP - Up
BGP summary information for VRF default for address-family: ipv4Unicast
Router ID: 10.0.22.11 Local AS: 65000
Neighbor AS State Up/DownTime BFD InMsgs OutMsgs InPfx OutPfx
10.0.22.1 65100 Estab 02:16:15 UP 1594 2004 6 6
10.0.23.1 65100 Estab 02:14:50 UP 1594 2002 6 12
The same occurs for other edge nodes.
Look that we are using the BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) on both BGP peers. The protocol BFD helps us to identify if the peer is alive or not.
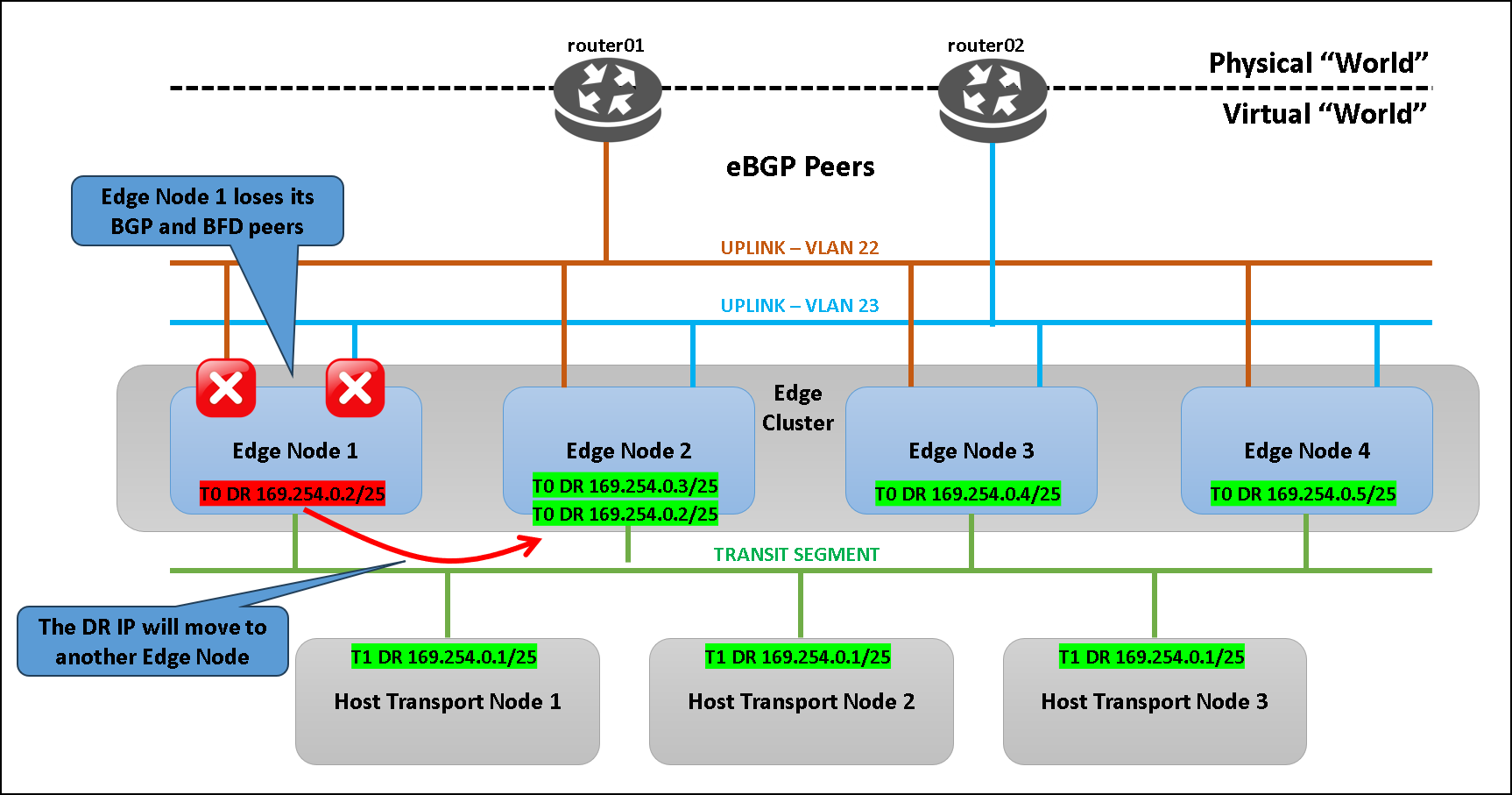
Simulating a Routing Failure on Edge-01
We will simulate a routing failure on the service router hosted on the edge transport node 01 (edge-01).
To simulate a routing failure, we will do:
- On each physical router, we will shut down (administratively) the BGP peer to the edge-01;
- And we will disable the BFD configuration on both physical routers as well.
What is the expected behavior?
The LIF (Logical Interface) on edge-01 will be moved temporarily to another edge transport node!
The picture below shows the failure scenario (in this example, the LIF interface from edge-01 is moving to edge-02. But, other edge nodes can be selected to receive this interface – this is an automatic process):
Checking the BGP peers on each physical router. Both peers 10.0.22.11 and 10.0.23.11 are to the edge-01 (from VLAN 22 and VLAN 23):
PHYSICAL ROUTER-01:
vyos@vyos-a:~$ show ip bgp summary
IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 192.168.255.8, local AS number 65100 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 35
RIB entries 21, using 4032 bytes of memory
Peers 7, using 143 KiB of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
10.0.20.2 4 65100 1706 1706 35 0 0 1d04h13m 10 10 N/A
10.0.21.2 4 65100 1706 1706 35 0 0 1d04h13m 10 10 N/A
10.0.22.11 4 65000 1591 1605 35 0 0 02:27:53 6 12 N/A
10.0.22.12 4 65000 1654 1665 35 0 0 1d03h22m 6 12 N/A
10.0.22.13 4 65000 1655 1662 35 0 0 1d03h21m 6 12 N/A
10.0.22.14 4 65000 1651 1662 35 0 0 1d03h21m 6 12 N/A
10.0.200.1 4 65100 1698 1707 35 0 0 1d04h14m 1 10 N/A
PHYSICAL ROUTER-02:
vyos@vyos-b:~$ show ip bgp summary
IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 192.168.255.9, local AS number 65100 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 35
RIB entries 21, using 4032 bytes of memory
Peers 7, using 143 KiB of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
10.0.20.1 4 65100 1707 1707 35 0 0 1d04h14m 10 10 N/A
10.0.21.1 4 65100 1707 1707 35 0 0 1d04h14m 10 10 N/A
10.0.23.11 4 65000 1606 1608 35 0 0 02:27:47 6 12 N/A
10.0.23.12 4 65000 1659 1666 35 0 0 1d03h23m 6 12 N/A
10.0.23.13 4 65000 1653 1665 35 0 0 1d03h23m 6 12 N/A
10.0.23.14 4 65000 1657 1665 35 0 0 1d03h23m 6 12 N/A
10.0.201.1 4 65100 1698 1707 35 0 0 1d04h14m 1 10 N/A
Disabling the BGP peers for the edge-01 and removing the BFD configuration as well.
Look the BGP peer is “Idle (Admin)”. It means that we disabled administratively this BGP peer:
PHYSICAL ROUTER-01:
set protocols bgp neighbor 10.0.22.11 shutdown
delete protocols bgp neighbor 10.0.22.11 bfd
vyos@vyos-a:~$ show ip bgp summary
IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 192.168.255.8, local AS number 65100 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 35
RIB entries 21, using 4032 bytes of memory
Peers 7, using 143 KiB of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
10.0.20.2 4 65100 1711 1711 35 0 0 1d04h18m 10 10 N/A
10.0.21.2 4 65100 1711 1711 35 0 0 1d04h18m 10 10 N/A
10.0.22.11 4 65000 1596 1610 0 0 0 00:00:10 Idle (Admin) 0 N/A
10.0.22.12 4 65000 1659 1670 35 0 0 1d03h27m 6 12 N/A
10.0.22.13 4 65000 1661 1668 35 0 0 1d03h27m 6 12 N/A
10.0.22.14 4 65000 1657 1668 35 0 0 1d03h27m 6 12 N/A
10.0.200.1 4 65100 1703 1712 35 0 0 1d04h19m 1 10 N/A
PHYSICAL ROUTER-02:
set protocols bgp neighbor 10.0.23.11 shutdown
delete protocols bgp neighbor 10.0.23.11 bfd
vyos@vyos-b:~$ show ip bgp summary
IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 192.168.255.9, local AS number 65100 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 35
RIB entries 21, using 4032 bytes of memory
Peers 7, using 143 KiB of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
10.0.20.1 4 65100 1713 1713 35 0 0 1d04h20m 10 10 N/A
10.0.21.1 4 65100 1713 1713 35 0 0 1d04h20m 10 10 N/A
10.0.23.11 4 65000 1613 1614 0 0 0 00:00:08 Idle (Admin) 0 N/A
10.0.23.12 4 65000 1665 1672 35 0 0 1d03h29m 6 12 N/A
10.0.23.13 4 65000 1659 1671 35 0 0 1d03h29m 6 12 N/A
10.0.23.14 4 65000 1663 1671 35 0 0 1d03h29m 6 12 N/A
10.0.201.1 4 65100 1704 1713 35 0 0 1d04h20m 1 10 N/A
Checking the BGP peer status on edge-01. Both peers are “Active” and not “Established”:
edge-01(tier0_sr[2])> get bgp neighbor summary
BFD States: NC - Not configured, DC - Disconnected
AD - Admin down, DW - Down, IN - Init, UP - Up
BGP summary information for VRF default for address-family: ipv4Unicast
Router ID: 10.0.22.11 Local AS: 65000
Neighbor AS State Up/DownTime BFD InMsgs OutMsgs InPfx OutPfx
10.0.22.1 65100 Activ 00:03:46 DC 1610 2043 0 0
10.0.23.1 65100 Activ 00:01:39 DC 1613 2032 0 0Now, accessing each edge transport node and seeing the backplane interfaces, we can see (in this case) that the LIF IP address has been assigned to the edge-03, as we can confirm in the following output:
Interface : 3aad399a-bb37-4d82-81d5-6111b4802863
Ifuid : 285
Name : bp-sr2-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-285
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.2/25;169.254.0.4/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5300/64(NA);fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5302/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:02
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : 61a1d1b8-3d43-4e01-80e2-1918213b055f
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :
With the above output, we confirmed that the LIF was moved to another edge transport node and the forwarding and routing processes can continue through this IP 169.254.0.2!
Removing the Routing Failure on Edge-01
As the routing peers on edge-01 can be recovered, the LIF IP address will move back to edge-01 immediately:
edge-01> get gateways
Wed Jan 31 2024 UTC 14:36:51.000
Gateway
UUID VRF Gateway-ID Name Type Ports Neighbors
736a80e3-23f6-5a2d-81d6-bbefb2786666 0 0 TUNNEL 3 3/5000
20169f10-8099-4d27-8915-8e1e0d47e68e 1 2050 DR-T0-GW DISTRIBUTED_ROUTER_TIER0 5 1/50000
c9e7c979-0d69-4aab-bd6c-9ee863c96070 2 3074 SR-T0-GW SERVICE_ROUTER_TIER0 7 5/50000
edge-01> get gateway 20169f10-8099-4d27-8915-8e1e0d47e68e interfaces
...
...
Interface : 6289a5dc-65c2-40a2-b6bc-53f3bd7b4770
Ifuid : 275
Name : bp-sr0-port
Fwd-mode : IPV4_ONLY
Internal name : downlink-275
Mode : lif
Port-type : backplane
IP/Mask : 169.254.0.2/25;fe80::50:56ff:fe56:5300/64(NA)
MAC : 02:50:56:56:53:00
VNI : 66561
Access-VLAN : untagged
Segment port : 1fb264c0-ecd6-4dcc-9856-0f759ec65e62
Urpf-mode : NONE
DAD-mode : LOOSE
RA-mode : RA_INVALID
Admin : up
Op_state : up
MTU : 1500
arp_proxy :
...
...
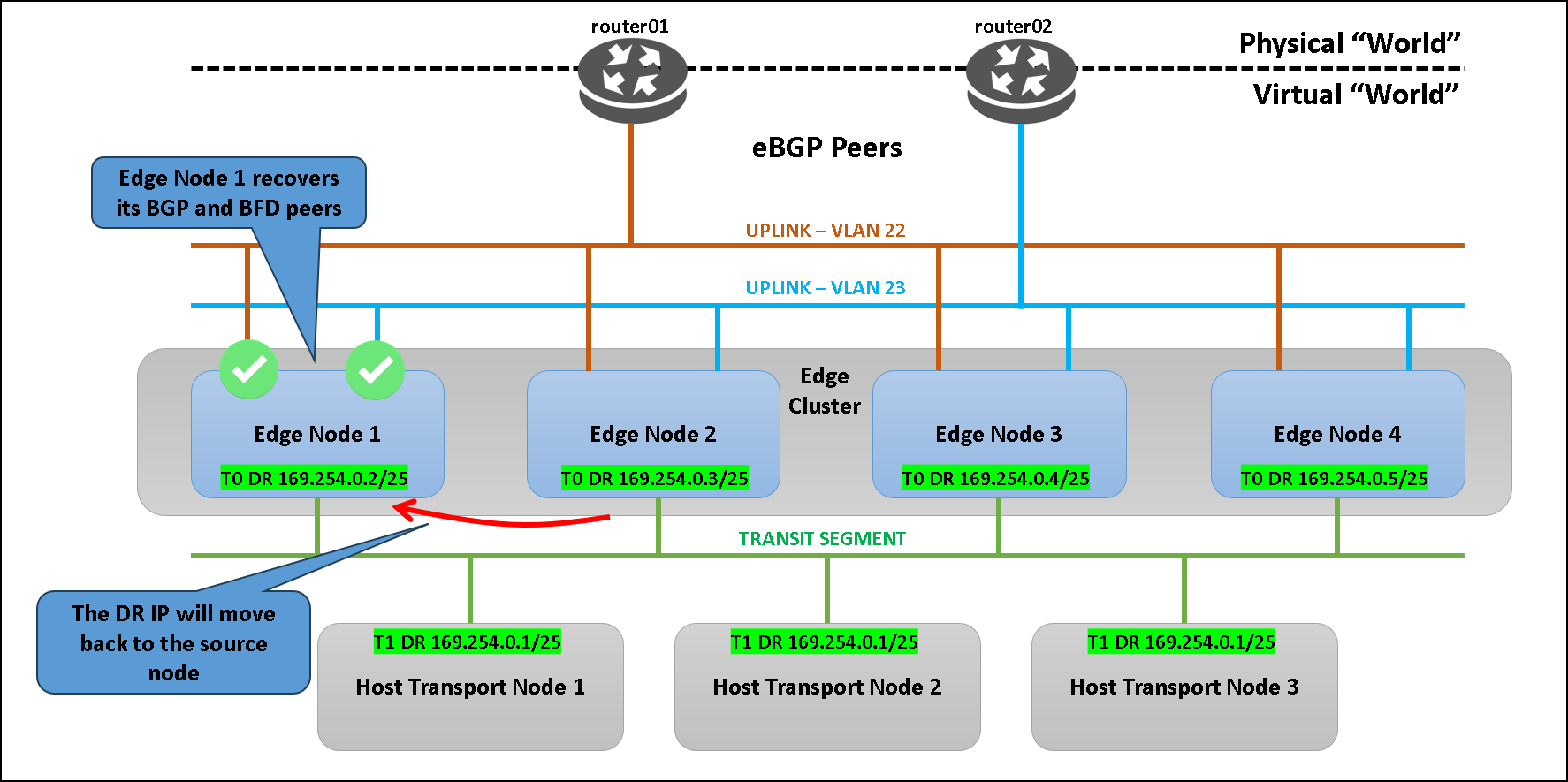
To Wrapping this Up
In this simple example, we can see what happens with the TO DR LIF interface when we have a routing issue. The LIF IP address is moved to another edge transport node just to avoid a massive update on all devices’ routing tables and it is an intelligent way to maintain the traffic flowing by this interface without interruption (or with minimal interruption).