vSphere HA Communication Network is an article that explains how vSphere HA Communication Network works in a vSAN Cluster, and what network is used to achieve that.
Definitely, the vSphere HA is a classical and useful feature present on the vSphere Stack.
vSphere HA provides high availability for virtual machines by pooling the virtual machines and the hosts they reside on into a cluster. Hosts in the cluster will monitor and in the event of a failure, the virtual machines on a failed host will restart on alternate hosts.
Note: It is very important here to avoid confusion or mistakes. When the vSphere HA detects a host failure or network partition, for example, all virtual machines running on this host will restart on other hosts on the vSphere Cluster.
We have an article that explains more detail about vSphere HA and, of course, how to enable vSphere HA. Click here to access this article.
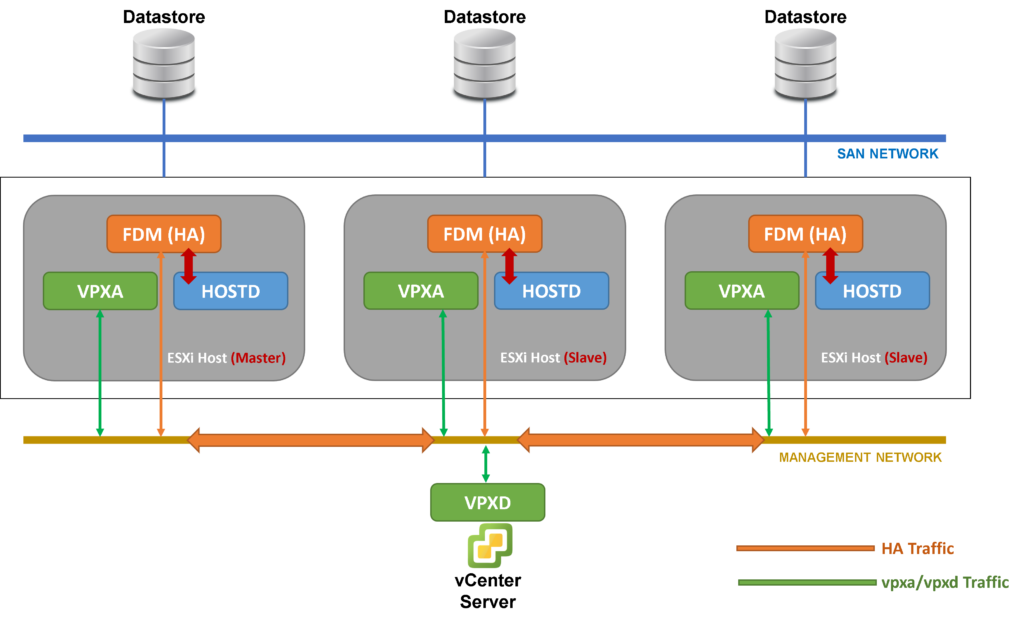
vSphere HA Communication Network: Management Network
When we have “Standard” vSphere Clusters or “3-2-1” environments (3 Hosts – 2 Switches – 1 Storage) and we need to use the vSphere HA service, the hosts inside this cluster will use the Management Network to exchange messages between each ESXi host as a Slave and between the ESXi host as a Master in vSphere HA with the vCenter Server.
In the picture below we can see how it works, for example:
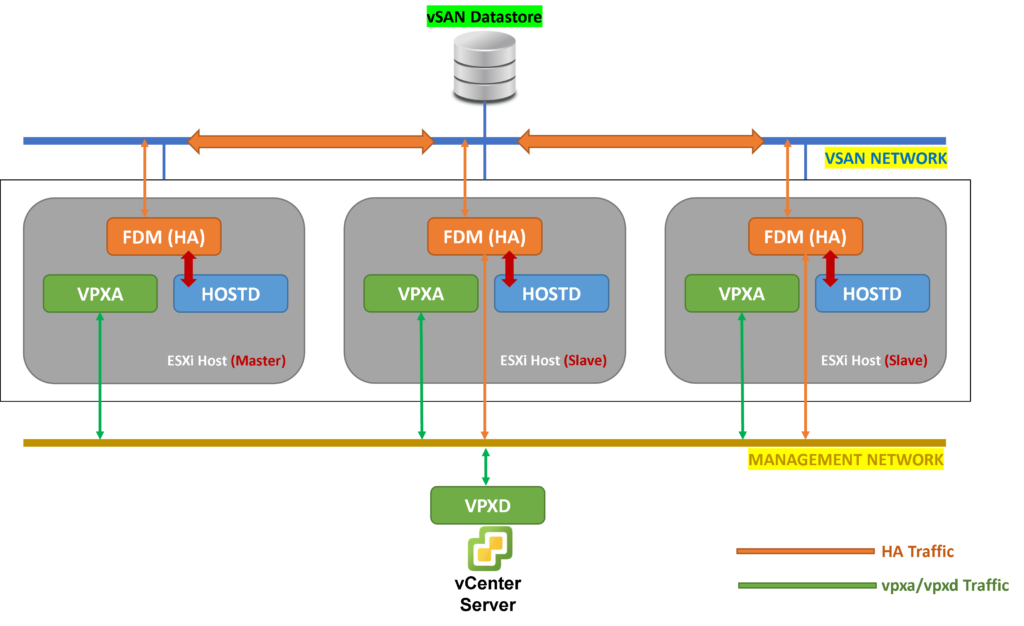
vSphere HA Communication Network: vSAN Network
However, when we have a vSAN Cluster and we need to use the vSphere HA, the network used by the vSphere HA service is the vSAN Network. This is because both services (vSAN and vSphere HA) are fully integrated and both need to work in a synchronous way.
For example:
In a vSAN Cluster with 3 ESXi hosts and with vSphere HA active, if one ESXi host fas a failure and the vSAN cluster is partitioned, the vSphere HA service needs to know that and to start the “restart process” of each VM on this failed host to other hosts in the cluster.
In the picture below we can see how it works through the vSAN Network:
Considerations for vSphere HA in a vSAN Cluster
So, the vSAN service can be configured first in the cluster. After that, we can configure the vSphere HA.
If the vSphere HA will be configured first than the vSAN service, an alert will be shown asking to disable the vSphere HA and, after enabling the vSAN service, enabling the vSphere HA again 🙂
Basically, we need to follow the below check-list:
1- Enable the vSAN service and make all vSAN configurations as needed;
2- After vSAN works fine, enable the vSphere HA and adjust the HA configuration according to your needs.
Isolation Detection Address – What is this?
The Isolation Detection Address is an IP that is used by the vSphere HA service to check if the host is isolated from the network. This IP is checked regularly by the vSphere HA service and, if these tests failed, the host is declared isolated and the vSphere HA can “restart” the VMs for other hosts in the cluster.
By default, the Gateway IP of the Management Network is used as Isolation Detection Address.
So, in a vSAN Cluster, is highly recommended to change the Isolation Detection Address for an IP on the vSAN Network (maybe we can use the Default Gateway of the vSAN Network, for example).
How to change the Isolation Detection Address?
On the vSphere HA Advanced Configurations, we can change the IP Address of the Isolation Detection Address.
Select the Cluster –> Configure –> Services –> vSphere Availability –> EDIT –> on Advanced Options, add the following entries:
das.useDefaultIsolationAddress=false
das.isolationAddress0=192.168.201.1
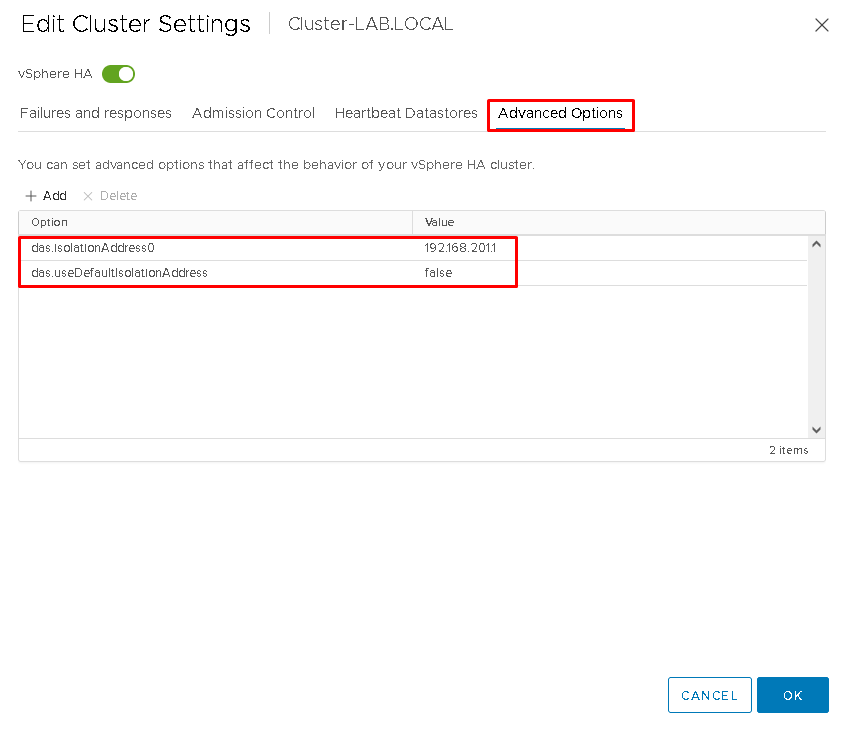
Click on OK to save. To check if the HA service is OK, disable and enable the HA service 🙂