Getting Started with TuneD on RHEL 8 demonstrates what the TuneD daemon is and how it can be used to optimize system performance.
So, what is the TuneD?
TuneD is a service/daemon that monitors your system and optimizes the performance under specific workloads. The core of TuneD are “profiles”, which tune your system for different use cases.
TuneD is distributed with many predefined profiles for use cases such as:
- High throughput
- Low latency
- Saving power
TuneD is a dynamic and static tuning tool that:
- Monitors system activity
- Applies predefined or custom tuning profiles
- Adjusts kernel parameters, CPU governors, disk I/O settings, and more
On RHEL 8, for instance, the TuneD is already installed and enabled by default:
systemctl status tuned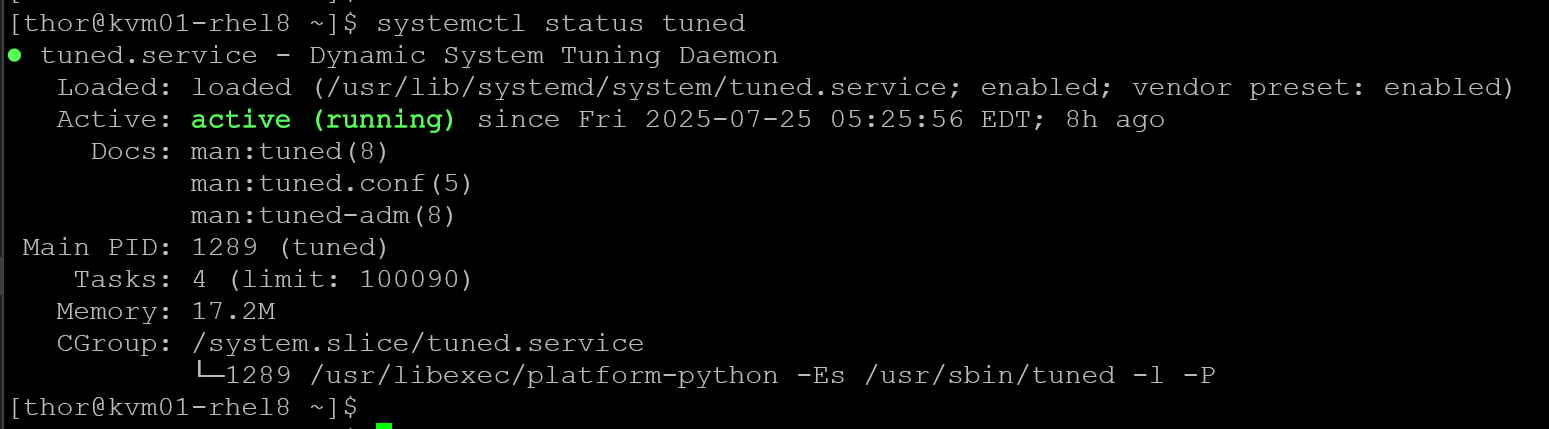
What Is It Used For?
TuneD helps system administrators:
- Improve performance for specific workloads (e.g., databases, virtual machines, network throughput)
- Reduce power consumption on idle or low-activity systems
- Automatically switch profiles based on system activity (dynamic tuning)
Common TuneD Profiles
A detailed analysis of a system can be very time-consuming. TuneD offers several predefined profiles for common use cases. You can also create, modify, and delete profiles.
Here are some of the most commonly used profiles:
| Profile Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
balanced | Balances performance and power saving |
throughput-performance | Optimized for high disk and network throughput |
latency-performance | Optimized for low latency; disables power-saving features |
powersave | Minimizes power usage; may reduce performance |
virtual-guest | Optimized for virtual machines |
virtual-host | Optimized for virtualization hosts |
desktop | Improves responsiveness for desktop environments |
oracle | Tuned for Oracle database workloads (requires extra package) |
Note: During system installation, the best profile for your system is automatically selected. Currently, the default profile is selected according to the following customizable rules:
| Environment | Default profile | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Compute nodes | throughput-performance | The best throughput performance |
| Virtual machines | virtual-guest | The best performance. If you are not interested in the best performance, you can change it to the balanced or powersave profile. |
| Other cases | balanced | Balanced performance and power consumption |
Dynamic vs Static Tuning
- Static tuning: Applies settings once at startup or when switching profiles
- Dynamic tuning: Continuously monitors system activity and adjusts settings in real time
Dynamic tuning can be enabled in /etc/tuned/tuned-main.conf by setting:
dynamic_tuning = 1How does dynamic tuning work?
- The
tuneddaemon monitors system components, such as CPU, disk, and network usage. - Based on activity levels, it adjusts system parameters to optimize performance or power efficiency.
- For example:
- If disk I/O is high, consider increasing the throughput settings.
- If the system is idle, it may reduce CPU frequency or disable unused devices to save power.
This enables the system to respond to changing workloads without requiring manual intervention.
How to Enable Dynamic Tuning?
1- Edit the main configuration file:
vi /etc/tuned/tuned-main.conf2- Set the following option:
[main]
dynamic_tuning = 1
update_interval = 10 # Optional: interval in seconds between tuning updates3- Restart the tuned service:
systemctl restart tunedNotes:
- Dynamic tuning is disabled by default.
- It’s not recommended for performance-critical environments, such as databases or real-time systems, where static tuning may be more predictable.
Basic tune-adm Commands
We can use the program “tune-adm” to manage details of the TuneD daemon:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
tuned-adm list | Lists all available tuning profiles |
tuned-adm active | Shows the currently active profile |
tuned-adm profile <name> | Activates the specified profile |
tuned-adm off | Disables all tuning and stops the tuned daemon |
tuned-adm recommend | Suggests the best profile for your system |
tuned-adm verify | Verifies that the current profile is correctly applied |
tuned-adm auto_profile | Enables automatic profile selection based on system characteristics |
tuned-adm profile_info <name> | Displays detailed information about a specific profile |
Let’s execute some commands to provide some examples.
1- List all available tuning profiles:
tuned-adm list
2- Shows the currently active profile:
tuned-adm active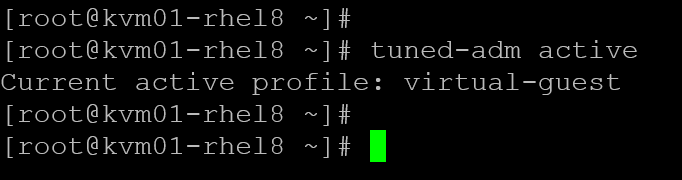
3- Check the best profile for your system:
tuned-adm recommend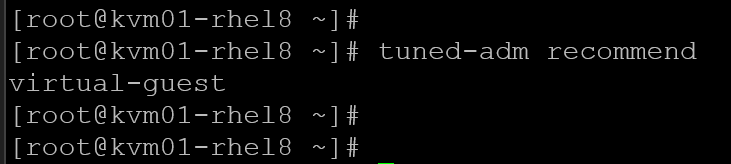
4- Get detailed information about a specific profile, for example, “hpc-compute”:
tuned-adm profile_info hpc-compute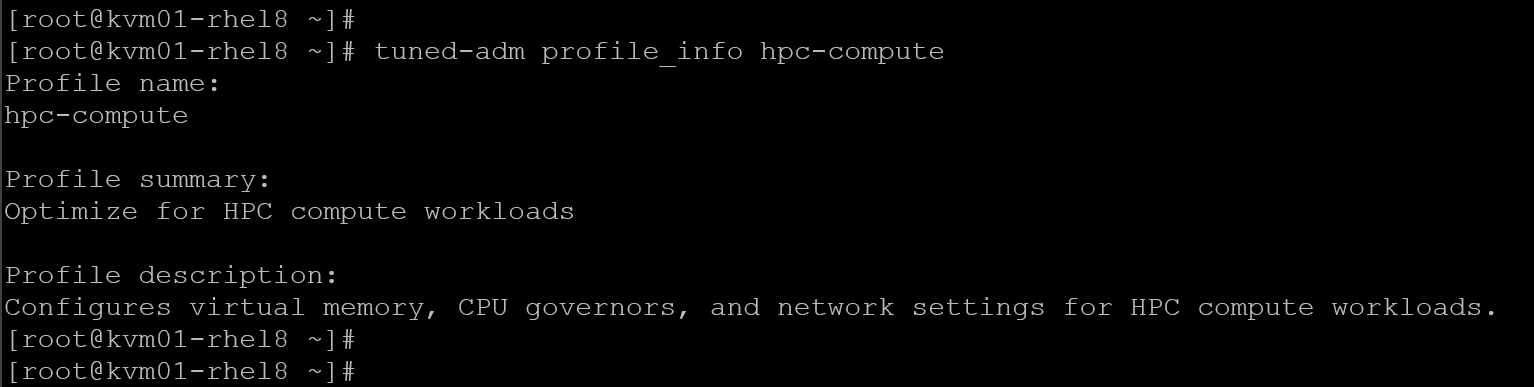
5- Check if the current profile is correctly applied:
tuned-adm verify
Default Log File Location
/var/log/tuned/tuned.logThis log file contains:
- Profile activation history
- Dynamic tuning decisions
- Errors or warnings during profile application
- Debug information (if enabled)
You can increase the logging level for troubleshooting by starting tuned with the --debug option or modifying its configuration:
tuned -DOr edit /etc/tuned/tuned-main.conf:
[main]
logging_level = DEBUGThen restart the service to apply the new configuration:
systemctl restart tunedThat’s it for now 🙂