Changing NTP Settings on ESXi Hosts is an article that shows an automated approach to changing the NTP client configurations on all connected ESXi hosts under the same vCenter Server, using a Python script.
The idea is to use a Linux CentOS 9 as a script server. We’ll execute a Python script from this server to connect to each ESXi host and upgrade the VMware Tools.
So, let’s get started:
1- Install CentOS 9 (without GUI) – We have tested it with CentOS 9, but feel free to install a different Linux flavor and adjust the script to run on it.
2- Access it by SSH with root rights and install Python:
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/danchiacchio/scripts/refs/heads/main/sh_PythonInstall/install-python.sh
chmod +x install-python.sh
./install-python.shGrab a coffee and wait for a while. The automated Python install takes a while to complete! ☕
3- Creating a working directory (something such as /root/scripts/py_vESXiNTPd) – you can choose the directory name:
mkdir -p /root/scripts/py_vESXiNTPd4- Go to the working directory and download the Python script “py_ESXiNTPd.py”:
cd /root/scripts/py_vESXiNTPd
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/danchiacchio/scripts/refs/heads/main/py_vESXiNTPd/py_ESXiNTPd.py
pip install pyvmomi paramiko5- Creating the NTP client configuration file:
touch ntp_config.txtAnd adding content into it – this is an example of NTP client configuration for an ESXi host – Adjust it to satisfy your needs:
restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict -6 ::1
driftfile /etc/ntp.drift
logconfig +clockstatus +peerstatus +sysstatus +syncstatus
server 192.168.255.3
tos maxdist 306- Run the Python script:
chmod 700 py_ESXiNTPd.py
python3 py_ESXiNTPd.py
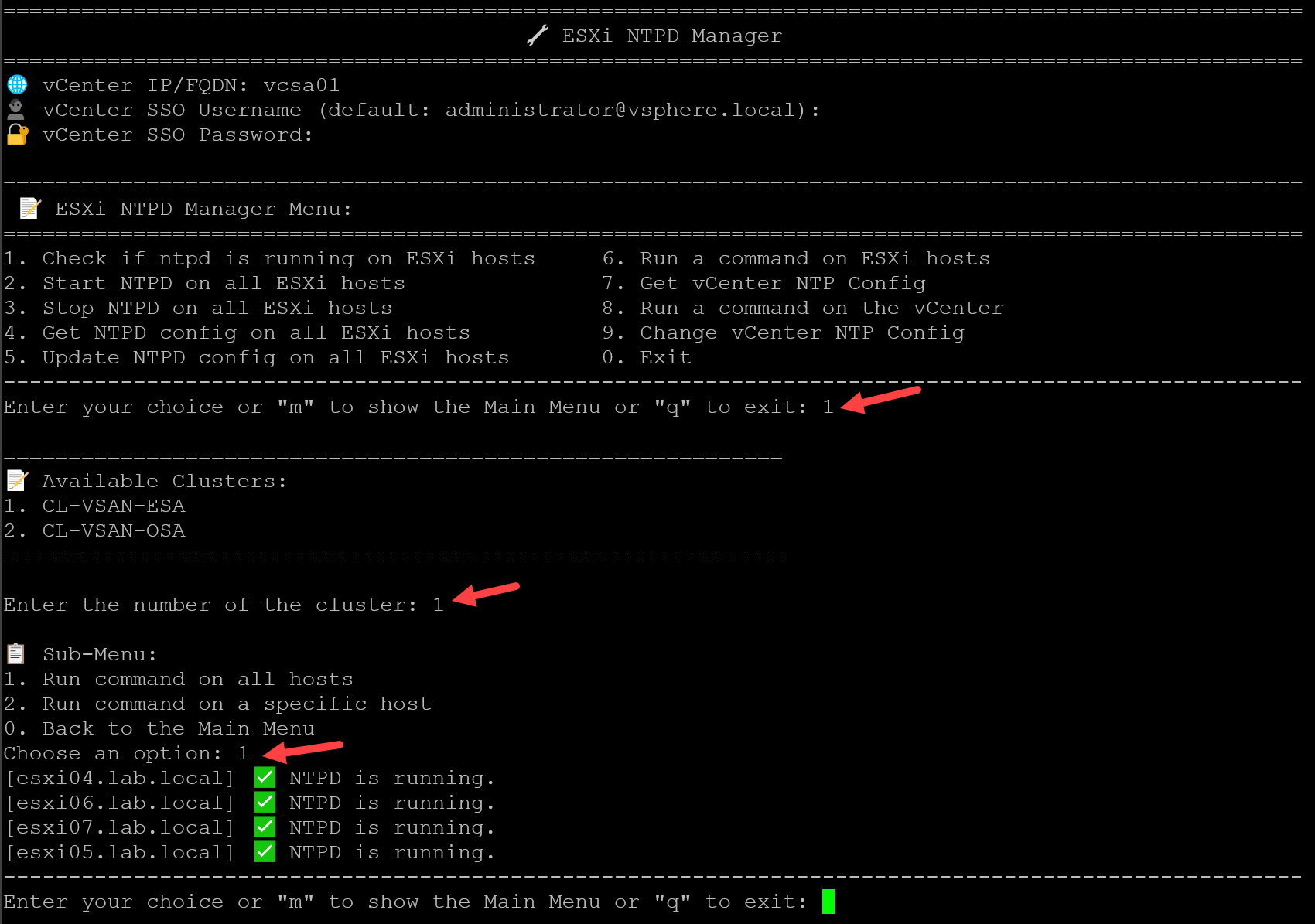
After running the script, for instance, we can get the ntpd status for hosts in a specific cluster:
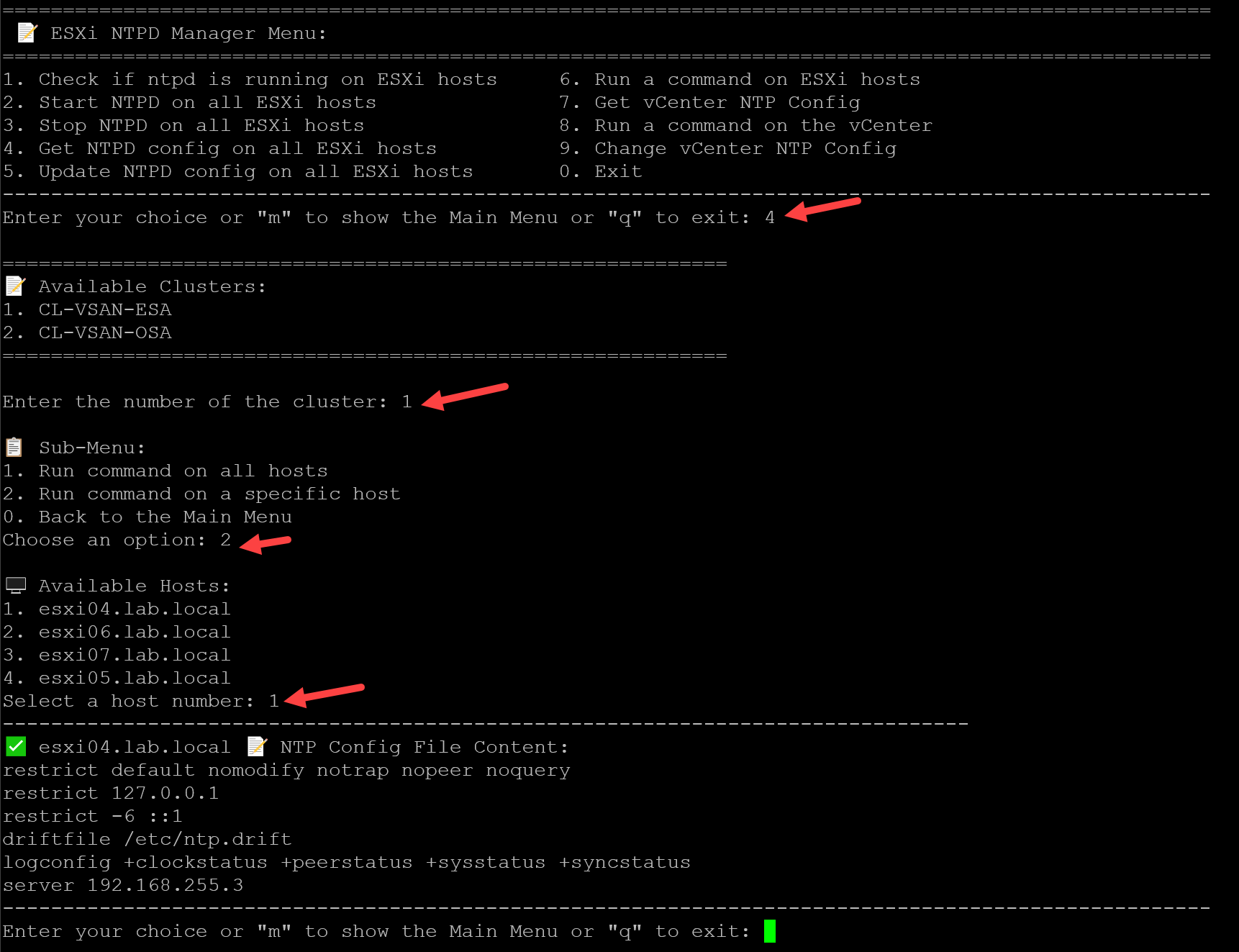
To get the NTP configuration for a particular ESXi host:
If you need to update or change the NTP configuration, you can select option five and specify the configuration file that you previously created!
This is a base-menu script, very user-friendly. So, explore the options to be familiar with them. If you have any doubts or improvements, feel free to contact me 😉
Note: So, I tested it several times in a lab environment, and it worked as expected. However, be careful when executing it in a production environment. We’ll not be responsible for downtime or weird behavior in your environment!