VMware Cloud Foundation is the next-generation VMware cloud platform for traditional and modern applications.
It is based on a proven and comprehensive software-defined stack, including VMware vSphere (ESXi + vCenter), VMware vSAN, VMware NSX, VMware vSphere with Tanzu, and the VMware Aria Suite.
With this software-based stack, VMware Cloud Foundation provides a complete service for an entire data center with computing, storage, network, container, and cloud management.
VMware Cloud Foundation Components
VMware Cloud Builder: This component is responsible for creating the VMware Cloud Foundation management domain. This virtual machine (VM) is deployed from an OVA file from Broadcom. It is used to deploy the management domain in a “bring-up” process. Consequently, the entire bring-up process is automated based on the Deployment Parameters Workbook file.
SDDC Manager: This component is deployed during the “bring-up” of the management domain. It is a Virtual Machine (VM) responsible for configuring and managing the entire environment. The SDDC Manager can perform all updates, patches, and configurations. So, it is vital to the Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) environment.
vSphere: The two core components here are ESXi and vCenter Server. ESXi is the hypervisor responsible for running VMs and the vCenter Server to manage multiple hosts. Particularly speaking, this is the base component of the VCF environment.
vSAN: Besides the fact that vSAN is placed in the ESXi kernel, it is considered an individual component because we can opt to use or not this component.
vSAN aggregates local or direct-attached storage devices to create a single storage pool named “vSAN Datastore.” All ESXi hosts contribute with their local disks to create the datastore. After that, the vSAN datastore can be used for all ESXi hosts in the vSAN cluster.
NSX: This component specifically focuses on providing networking, security, automation, and operational simplicity for applications running in a virtual environment. An overlay network is created over the physical networking, and all virtualized traffic flows through it.
NSX offers a series of features. An example is the micro-segmentation feature (it is possible to block VM-to-VM communication in the same broadcast domain – the same layer two domain).
vSphere with Tanzu: When enabled on a vSphere cluster, vSphere with Tanzu allows you to run Kubernetes workloads directly on ESXi hosts and create upstream Kubernetes clusters within dedicated resource pools.
VMware Aria Suite: Finally, within VCF, an automated deployment of VMware Aria Suite is possible. VMware Aria Suite is a stack of software for VMware Aria Operations for Logs, VMware Aria Automation, and VMware Aria Operations. This software stack allows complete control and management of the entire VCF environment.
VMware Cloud Foundation Architectures
VCF consists of workload domains (VCF is made of workload domains). A workload domain represents a logical unit that groups ESXi hosts managed by a vCenter with specific characteristics and best practices by VMware. (In my mind, a workload domain is a vSphere Cluster). So, there are two VCF architectures: Standard and Consolidated.
Standard: The standard architectural model is the recommended model by VMware. In this model, we have a dedicated management domain to host all management VMs (vCenter, NSX Manager Cluster, etc.) and dedicate workload domains to run users’ workloads (named Virtual Infrastructure or VI).
A dedicated vCenter Server instance is necessary for each VI workload domain. The same is true for the NSX Manager. An NSX Manager cluster is created for each VI workload domain, and all run on the management workload domain.
However, VMs for the NSX Edge cluster run on the VI workload domain (an NSX Edge Cluster is necessary to provide North-South connectivity):
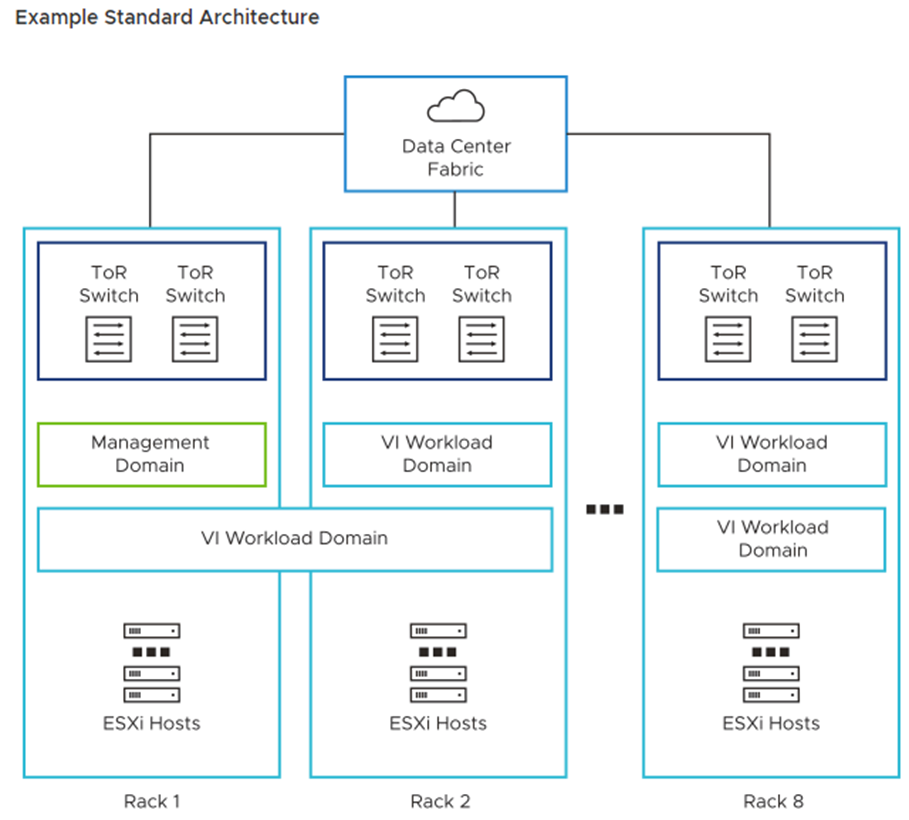
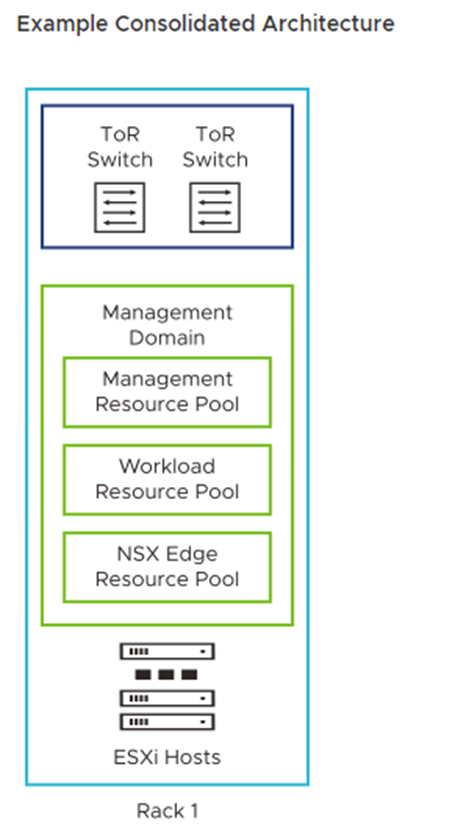
Consolidated: In this model, the management and user workloads run together on the same workload domain (they share the same resources). During the “bring-up,” beyond creating the management domain, a vSphere resource pool is created to segregate the user’s virtual machines. It is not the best model recommended by VMware. However, it can be used for proof-of-concept, lab, and small environments:
To Wrapping This Up
In conclusion, VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) is a transformative solution that provides a streamlined approach to hybrid cloud computing.
By integrating compute, storage, networking, and security capabilities into one software stack, VCF simplifies the deployment and operation of a consistent and secure infrastructure across private and public clouds.
This empowers businesses to improve agility, efficiency, and flexibility in their IT operations, enabling them to focus more on innovation and less on maintaining infrastructure.
As we move forward in the digital age, solutions like VCF will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of cloud computing.