Creating a Simple Python Project Using a Virtual Environment demonstrates, in practice, how to use a virtual environment.
First and foremost, we’ve written an article to explain how to install Python on Windows. Click here to access this article.
Additionally, if you’re not familiar with Python virtual environment (venv), there is an article to explain it a bit. Click here to access this article.
Important note: We're running Python on Windows. However, I thing that all the steps can work on Linux (feel free to test it on Linux)!Let’s Get Started: The Python Directory
After installing Python (on Windows, Linux, or any operating system), a good practice is to create a directory to store your Python projects. In our case, for instance, since we’re on Windows, a Python directory could be:
C:\pythonTo create it, open the cmd and execute the following command:
mkdir C:\pythonCreating the Project
So, now, let’s create our project from scratch. In this case, for instance, we’ll create an SSH runner project to run commands on a remote host through an SSH connection:
1. Create the project directory inside the Python directory:
mkdir C:\python\py-ssh-runner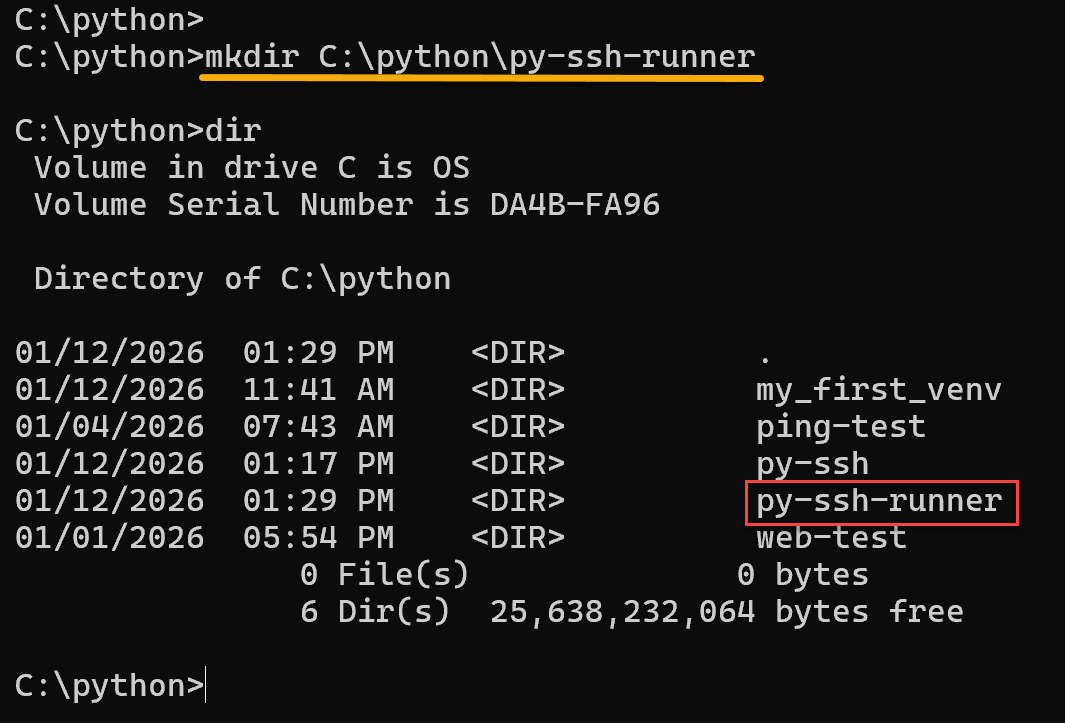
2. Access the project directory and create the Python virtual environment (venv):
cd C:\python\py-ssh-runner
python -m venv venv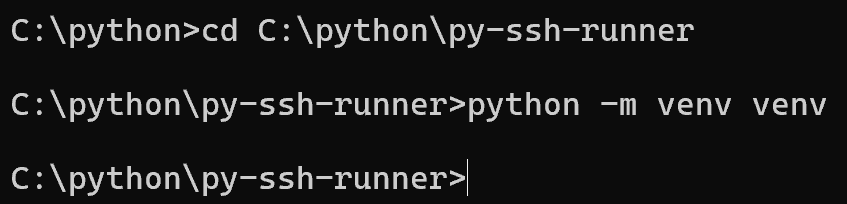
3. Activate the virtual environment:
venv\Scripts\activate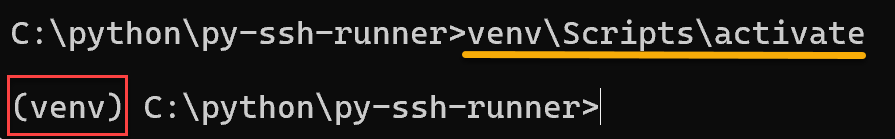
Note: Look at the command prompt. The “venv” name must be shown!
4. Install SSH Module/Library (paramiko):
pip install paramiko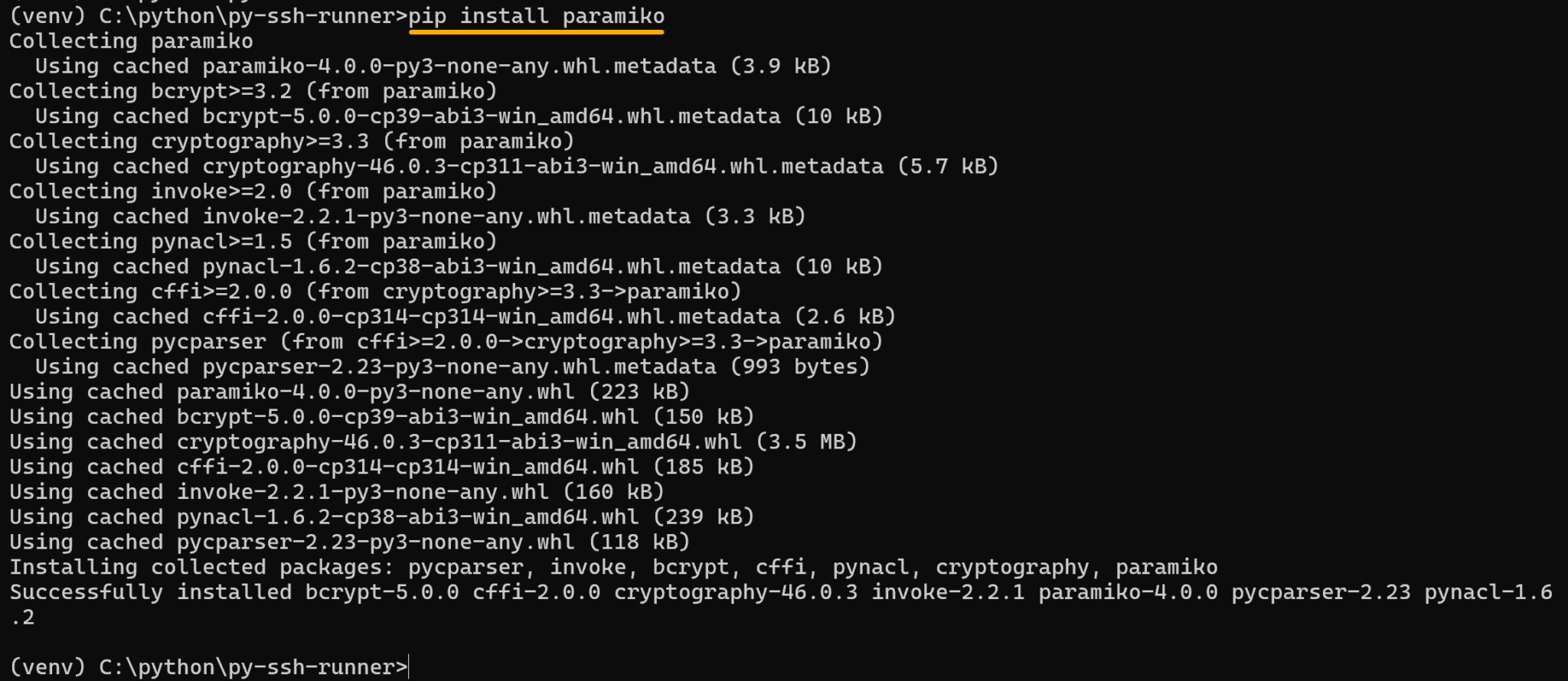
To confirm it paramiko was installed successfully:
pip list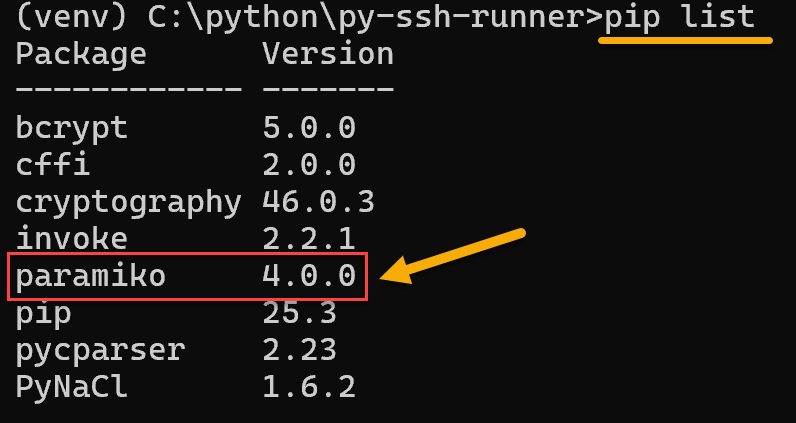
5. Create the SSH script:
notepad ssh_runner.pyAnd add the following content. After that, save the file and close the notepad application:
import paramiko
from getpass import getpass
host = input("Host: ")
user = input("User: ")
password = getpass("Password: ")
command = input("Command: ")
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(hostname=host, username=user, password=password)
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command(command)
print(stdout.read().decode())
print(stderr.read().decode())
ssh.close()6. Execute the SSH script:
python ssh_runner.pyThe script will ask for hostname or IP, username, password, and the command that you wanna to run on the remote host. For example:
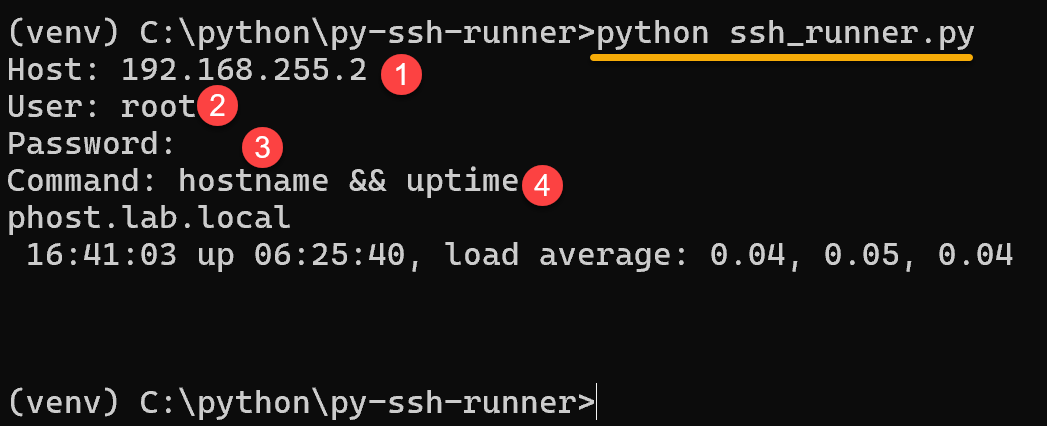
7. To correctly exit the virtual environment:
deactivate
That’s it for now 😉